|
|
Employee - базов
клас, Manager -
производен клас
- членовете-данни на базовият клас са членове-данни и на
производния клас (всеки обект от производния клас съдържа данните
на базовия клас);
- функциите на производният клас нямат достъп до
частните членове на базовия клас.
** Дефиниции на функции в производния клас
Конструкторът на производния клас има две задачи:
- да инициализира полетата с данни, дефинирани в производния клас;
- да инициализира обекта от базовия клас, който се съдържа в
обекта от производния клас.
Manager::Manager(string n, double sal, string dept)
:
Employee(n, sal)
{ department = dept; }
Ако в базовия и в производния класове има функции с едно и също
име (напр. print()), то викането на член-функция
на базовия клас от функция на производния клас става с помощта на
операция "принадлежност към клас" (::).
void Manager::print()
{
Employee::print();
cout <<
department;
}
// manager.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Employee {
public:
Employee(string emp_name, double
init_salary);
void set_salary(double new_salary);
string get_name() const;
double get_salary() const;
void print() const;
private:
string name;
double salary;
};
class Manager : public Employee {
public:
Manager(string n, double sal, string
dept);
string get_department() const;
void print() const;
private:
string department;
};
int main()
{
Employee harry("Harry", 500);
harry.set_salary(550);
harry.print();
cout << harry.get_salary()
<< endl;
Manager nino("Nino", 670, "Computer
Science");
nino.set_salary(1200);
nino.print();
cout << nino.get_salary()
<< " "
<<
nino.get_department() << endl;
return 0;
}
Employee::Employee(string emp_name, double init_salary)
{
name = emp_name;
salary = init_salary;
}
void Employee::set_salary(double new_salary)
{
salary = new_salary;
}
string Employee::get_name() const
{
return name;
}
double Employee::get_salary() const
{
return salary;
}
void Employee::print() const
{
cout << get_name() << " "
<< salary << endl;
}
Manager::Manager(string n, double sal, string dept)
: Employee(n, sal)
{
department = dept;
}
string Manager::get_department() const
{
return department;
}
void Manager::print() const
{
Employee::print();
cout << department <<
endl;
}
| Harry 550 550 Nino 1200 Computer Science 1200 Computer Science |
// clock1.cpp}
#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <string> using namespace std; #include "ccc_time.h" class Clock { public: /** Constructs a clock that can tell the local time. @param use_military true if the clock uses military format (21:05) and
flase if the clock uses "am/pm" format (9:05 pm) */ Clock(bool use_military); /** Gets the location of this clock. @return the location */ string get_location() const; /** Gets the hours of this clock. @return the hours, in military or am/pm format */ int get_hours() const; /** Gets the minutes of this clock. @return the minutes */ int get_minutes() const; /** Checks whether this clock uses miltary format. @return true if miltary format */ bool is_military() const; private: bool military; }; Clock::Clock(bool use_military) { military = use_military; } string Clock::get_location() const { return "Local"; } int Clock::get_hours() const { Time now; int hours = now.get_hours(); if (military) return hours; if (hours == 0) return 12; else if (hours > 12) return hours - 12; else return hours; } int Clock::get_minutes() const { Time now; return now.get_minutes(); } bool Clock::is_military() const { return military; } int main() { Clock clock1(true); Clock clock2(false); bool more = true; while (more) { cout << "Military time: " << clock1.get_hours() << ":" << setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clock1.get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n"; cout << "am/pm time: " << clock2.get_hours() << ":" << setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clock2.get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n"; cout << "Try again? (y/n) "; string input; getline(cin, input); if (input != "y") more = false; } return 0;
| nkirov@cpp % c++
clocks1.cpp ccc_time.cpp nkirov@cpp % ./a.out Military time is 9:33 am/pm time is 9:33 Try again? (y/n) y Military time is 9:33 am/pm time is 9:33 Try again? (y/n) n nkirov@cpp % |
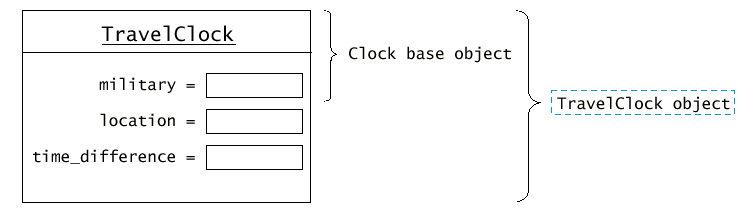
TravelClock clock("London", -2);
cout << "The time in " << clock.get_location() << " is "
<< clock.get_hours() << ":" << clock.get_minutes();
Обект от TravelClock (производния клас) има 3 разлики с
обект от Clock:class TravelClock : public Clock {
public:
TravelClock(bool mil, string loc, double off);
int get_hours() const;
string get_location() const;
private:
string location;
int time_difference;
};
TravelClock::TravelClock(bool mil, string loc, int diff)Ако не се извика (явно) конструктора на базовия клас, обектът от производния клас се създава, като автоматично (неявно) се вика конструктора по подразбиране на базовия клас.
: Clock(mil)
{ location = loc;
time_difference = diff;
while (time_difference < 0)
time_difference = time_difference + 24;
};
int TravelClock::get_hours() const
{ . . .
int h = Clock::get_hours(); /* calls base-class function */
. . .
}
// clock2.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#include "ccc_time.h"
class Clock {
public:
Clock(bool use_military);
string get_location() const;
int get_hours() const;
int get_minutes() const;
bool is_military() const;
private:
bool military;
};
Clock::Clock(bool use_military)
{ military = use_military; }
string Clock::get_location() const
{ return "Local"; }
int Clock::get_hours() const
{ Time now;
int hours = now.get_hours();
if (military) return hours;
if (hours == 0) return 12;
else if (hours > 12) return hours - 12;
else return hours;
}
int Clock::get_minutes() const
{ Time now;
return now.get_minutes();
}
bool Clock::is_military() const
{ return military; }
class TravelClock : public Clock {
public:
/**
Constructs a travel clock that can tell the time
at a specified location
@param mil true if the clock uses military format
@param loc the location
@param diff the time difference from the local time
*/
TravelClock(bool mil, string loc, int diff);
string get_location() const;
int get_hours() const;
private:
string location;
int time_difference;
};
TravelClock::TravelClock(bool mil, string loc, int diff)
: Clock(mil)
{ location = loc;
time_difference = diff;
while (time_difference < 0)
time_difference = time_difference + 24;
}
string TravelClock::get_location() const
{ return location; }
int TravelClock::get_hours() const
{ int h = Clock::get_hours();
if (is_military())
return (h + time_difference) % 24;
else
{ h = (h + time_difference) % 12;
if (h == 0) return 12;
else return h;
}
}
int main()
{
Clock clock1(true);
cout << clock1.get_location() << " time: "
<< clock1.get_hours() << ":"
<< setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clock1.get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n";
TravelClock clock2(true, "Rome", -1);
cout << clock2.get_location() << " time: "
<< clock2.get_hours() << ":"
<< setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clock2.get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n";
TravelClock clock3(false, "Tokyo", 5);
cout << clock3.get_location() << " time: "
<< clock3.get_hours() << ":"
<< setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clock3.get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n";
return 0;
}
| Local time is 9:36 Rome time is 8:36 Tokyo time is 2:36 |
vector<Clock> clocks(3);[ clocks2a.cpp ]
/* populate clocks */
clocks[0] = Clock(true);
clocks[1] = TravelClock(true, "Rome", -1);
clocks[2] = TravelClock(false, "Tokyo", 5);
for (int i = 0; i < clocks.size(); i++)
cout << clocks[i].get_location() << " time: "
<< clocks[i].get_hours() << ":"
<< setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clocks[i].get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n";
Local time is 21:15 |
vector<Clock*> clocks(3);Векторът clocks съдържа колекция от различни часовници - указатели към обекти от различни класове. Такава колекция се нарича полиморфна.
/* populate clocks */
clocks[0] = new Clock(true);
clocks[1] = new TravelClock(true, "Rome", -1);
clocks[2] = new TravelClock(false, "Tokyo", 5);
for (int i = 0; i < clocks.size(); i++)
cout << clocks[i]->get_location() << " time: "
<< clocks[i]->get_hours() << ":"
<< setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clocks[i]->get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n";
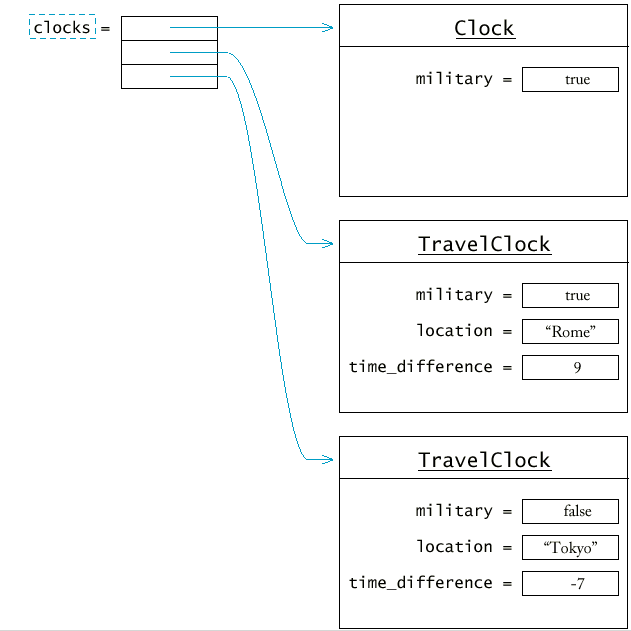
Local time is 21:15 |
class Clock {Програмата с динамично свързване:
public:
Clock(bool use_military);
virtual string get_location() const;
virtual int get_hours() const;
int get_minutes() const;
bool is_military() const;
private:
. . .
};
// clocks3.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <string> #include <vector> using namespace std; #include "ccc_time.h" class Clock { public: Clock(bool use_military); virtual string get_location() const; virtual int get_hours() const; int get_minutes() const; bool is_military() const; private: bool military; }; Clock::Clock(bool use_military) { military = use_military; } string Clock::get_location() const { return "Local"; } int Clock::get_hours() const { Time now; int hours = now.get_hours(); if (military) return hours; if (hours == 0) return 12; else if (hours > 12) return hours - 12; else return hours; } int Clock::get_minutes() const { Time now; return now.get_minutes(); } bool Clock::is_military() const { return military; } class TravelClock : public Clock { public: TravelClock(bool mil, string loc, int diff); string get_location() const; int get_hours() const; private: string location; int time_difference; }; TravelClock::TravelClock(bool mil, string loc, int diff) : Clock(mil) { location = loc; time_difference = diff; while (time_difference < 0)
time_difference = time_difference + 24; } string TravelClock::get_location() const { return location; } int TravelClock::get_hours() const { int h = Clock::get_hours(); if (is_military()) return (h + time_difference) % 24; else { h = (h + time_difference) % 12; if (h == 0) return 12; else return h; } } int main() { vector<Clock*> clocks(3); clocks[0] = new Clock(true); clocks[1] = new TravelClock(true, "Rome", -1); clocks[2] = new TravelClock(false, "Tokyo", 5); for (int i = 0; i < clocks.size(); i++) { cout << clocks[i]->get_location() << " time: "
<< clocks[i]->get_hours() << ":" << setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clocks[i]->get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n"; } return 0; }
| Local time is 18:07 Rome time is 17:07 Tokyo time is 11:07 |