lec6
6. Fibonacci Series..
Greatest common divisor, least common multiple. Recursion
Fibonacci
numbers (YouTube)
1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, ...
F(0) = F(1) = 1
F(n+1) = F(n-1) + F(n) , n > 1
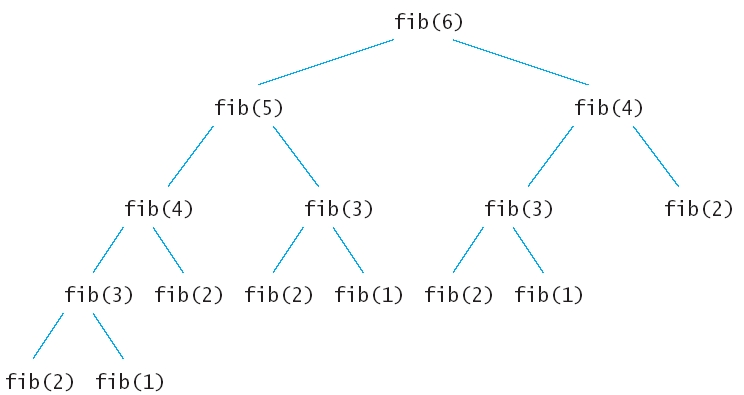
int fib(int n)
{ if (n <= 2)
return 1;
else return
fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
}
int fib(int n)
{ cout << "Entering fib: n = " << n << "\n";
int f;
if (n <= 2) f = 1;
else f = fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
cout << "Exiting fib: n = " << n
<< " return value = " << f << "\n";
return f;
}
int fib(int n)
{ if (n <= 2) return 1;
int fold = 1;
int fold2 = 1;
int fnew;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
{ fnew = fold + fold2;
fold2 = fold;
fold = fnew;
}
return fnew;
}
** Greatest
common divisor [1.2.3]
* Euclid's algorithm for finding the largest common divisor
// gcd.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
unsigned
gcd1(unsigned a, unsigned b)
{ unsigned swap;
while (b > 0) { swap = b; b =
a%b; a = swap; }
return a;
}
unsigned
gcd2(unsigned a, unsigned b)
{ return (0 == b) ? a : gcd2(b, a%b); }
int main()
{ const unsigned a = 1, b = 125;
cout << gcd1(a, b) <<
endl;
cout << gcd2(a, b) <<
endl;
return 0;
* To implement the algorithm by subtraction only.
** Return from recursion and us of variables [1.2.5]
* Recursively printing the digits of a number
//
digit2.cpp
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
void
printN(unsigned n)
{ if (n >= 10) printN(n/10);
cout << n%10;;
}
int main()
{ unsigned m = 1234;
printN(m);
return 0;
}
* Calculating n! [1.2.5]
// fact.cpp
#include <iostream>
unsigned long
fact1(unsigned i)
{ if (1 == i) return 1;
return i * fact1(i
- 1);
}
unsigned i;
unsigned long fact2()
{
if (1 == i) return 1;
return i-- * fact2(); //
--i*fact();
}
const unsigned n = 6;
int main()
{
std::cout
<< "fact1: " << n << "! = " <<
fact1(n) << endl;
i=n; // i=n+1;
std::cout <<
"fact2: " << n << "! = " << fact2(n)
<< endl;
return 0;
}
** Recursion and use of
global variables [1.2.5]
* For a given integer n (n <9), print
in ascending and descending order the numbers 10k (0 < k < n).
// print0.cpp
#include
<iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
const unsigned n = 6;
void printRed1(unsigned k,
unsigned long res)
{ cout << res
<< " ";
if (k < n)
printRed1(k + 1, res*10);
cout << res
<< " ";
}
unsigned k = 0;
void printRed2(unsigned long res)
{ k++;
cout << res << " ";
if (k < n) printRed2(res*10);
cout << res << " ";
}
unsigned
long res = 1;
void printRed3()
{ k++;
res *= 10;
cout << res << "
";
if (k < n)
printRed3();
cout << res << "
";
res /= 10;
}
int main()
{
printRed1(1,10); cout << endl;
printRed2(10); cout << endl;
k = 0;
printRed3(); cout << endl;
return 0;
}
