4. Потоци I
 Пренасочване на входния и изходния потоци.
Пренасочване на входния и изходния потоци.
C:\my\>myprog <
a_cin.txt
Вместо от клавиатурата, операционната система пренасочва
входа от текстов файл, в случая това е файла a_cin.txt.
C:\my\>myprog >
a_cout.txt
Вместо на екрана, операционната система пренасочва изхода
на текстов файл, в случая това е файла a_cout.txt.
// words.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ int count = 0;
string word;
while (cin >> word) count++;
cout << count << " words.\n";
return 0;
}
С пренасочване на входа програмата words за намиране на броя на думите може намери броя на думите в текстов
файл (едно по-смислено приложение на тази програма).
Четене на редове:
// lines.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ int count = 0;
string lines;
while (getline(cin, lines)) count++;
cout << count << " lines.\n";
return 0;
}
Четене на символи (букви, цифри и специални символи):
// chars.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ int count = 0;
char ch;
while (cin.get(ch)) count++;
cout << count << " chars.\n";
return 0;
}
 Четене и
запис в текстови файлове.
Четене и
запис в текстови файлове.
** В заглавния файл fstream
са дефинирани обекти, функции и операции за работа с файлове.
А) Четене от файл.
* Дефиниране на файлова променлива за четене - обект от класа ifstream:
ifstream inp_data;
* Отваряне на файл от текущата директория с име input.dat:
inp_data.open("input.dat");
* Четене от файл на:
- цели числа и числа с плаваща точка
int n;
double x;
inp_data >> n
>> x;
- низове
string s;
inp_data >>
s; // чете до
разделител
getline(inp_data, s); //
чете цял ред
- символи
char ch;
inp_data.get(ch); // чете един символ
inp_data.unget(); // връща последния
прочетен символ в буфера
* затваряне на файл
inp_data.close();
Пример:
// readf.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include
<fstream>
/*
включване на заглавен файл */
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ ifstream in_data; /*
дефиниране на файлова променлива за четене */
in_data.open("readf.txt"); /* отваряне на файла
readf.txt */
string s1, s2;
getline(in_data,
s1); /* четене на ред */
in_data >>
s2;
/*
четене на дума */
int n;
double x;
in_data >> n
>>
x; /*
четене на числови данни */
char ch;
while (!in_data.eof())
in_data.get(ch);
/* четене на символ */
in_data.close();
/*
затваряне на файла */
cout << s1
<< endl << s2 << " "
<<
n << " " << x << " " << ch <<
endl;
return 0;
}
Файл readf.txt:
many happy words
one_word 123
9.98 N |
many happy words
one_word 123
9.98 N |
Пример:
// maxval1.cpp
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
/**
Reads numbers from a file and finds the
maximum value
@param in the input stream to read from
@return the maximum value or 0 if the file
has no numbers
*/
double read_data(ifstream& in)
{ double highest;
double next;
if (in >> next) highest = next;
else return 0;
while (in >> next)
if (next > highest) highest =
next;
return highest;
}
int main()
{ string filename;
cout << "Please enter the data file
name: ";
cin >> filename;
ifstream infile;
infile.open(filename.c_str());
if (infile.fail())
{ cout << "Error opening "
<< filename << "\n";
return 1;
}
double max = read_data(infile);
cout << "The maximum value is "
<< max << "\n";
infile.close();
return 0;
}
Пример: Отделяне на цифрови от текстови данни.
// readfile.cpp
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ cout << "Enter the file name: ";
string fname;
cin >> fname;
ifstream infile;
infile.open(fname.c_str());
if (infile.fail())
{ cout << "ERROR";
return
1;
}
int sum = 0;
while (!infile.eof())
{ char ch;
infile.get(ch);
if ('0' <= ch
&& ch <= '9') /* it was a digit */
{
infile.unget(); /* oops - didn't want to read it */
int n;
infile >> n; /* read integer starting with ch */
sum += n;
}
else cout
<< ch;
}
infile.close();
cout << "The sum is "
<< sum << endl;
return 0;
}
Б) Писане във файл.
* дефиниране на файлова променлива за писане - обект от класа ofstream:
ofstream out_data;
* отваряне на файл
out_data.open("output.dat");
* писане във файл с:
- изходен поток
int n = 2;
double x = 1.5;
string s = " Hello";
out_data << n
<< " " << x << s;
- член-функция
char ch = 'A';
out_data.put(ch);
* затваряне на файл
out_data.close();
Пример:
// writef.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include
<fstream>
/*
включване на заглавен файл */
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ ofstream out_data; /*
дефиниране на файлова променлива за писане */
out_data.open("writef.txt"); /* отваряне на файла
writef.txt */
string s = "Hello";
out_data << s
<< endl; /* писане на низ */
int n = 5;
double x = 5.5;
out_data << n
<< " " << x << " "; /* писане на числови
данни */
char ch = 'T';
out_data.put(ch); /*
писане на символ */
out_data.close();
/*
затваряне на файла */
return 0;
}
Файл writef.txt:
Пример: Отделяне на цифрови от текстови данни и записване на числата
във файл.
// readwritefiles.cpp
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ cout << "Enter the input file name: ";
string finame;
cin >> finame;
ifstream infile;
infile.open(finame.c_str());
if (infile.fail())
{ cout << "Error opening " << finame << endl;
return 1;
}
cout << "Enter the output file name: ";
string foname;
cin >> foname;
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open(foname.c_str());
if (outfile.fail())
{ cout << "Error opening " << foname << endl;;
return 1;
}
while (!infile.eof())
{ char ch;
infile.get(ch);
if ('0' <= ch && ch <= '9') /* it was a digit */
{ infile.unget(); /* oops - didn't want to read it */
int n;
infile >> n; /* read integer starting with ch */
outfile << n << endl;
}
else cout << ch;
}
infile.close();
outfile.close();
return 0;
}
** Йерархия на потоковите класове
* Потоковата библиотека на С++ се състои от няколко класове,
свързани в следната йерархия:
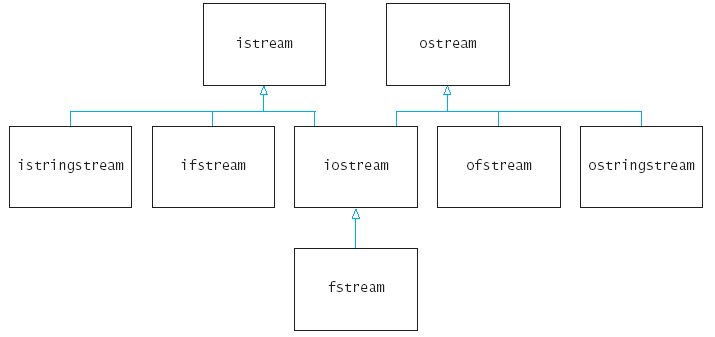
* Обектите cin и cout са от класове, които са системно
зависими и нямат стандартни имена, но са производни класове
съответно на istream и ostream. Затова можем да дефинираме:
double read_data(istream& in);
и след това да извикаме функцията с параметри от различни
производни на istream класове: .
max = read_data(infile);
max = read_data(cin);
Пример:
// maxval2.cpp
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
/**
Reads numbers from a file and finds the maximum value
@param in the input stream to read from
@return the maximum value or 0 if the file has no numbers
*/
double read_data(istream& in)
{ double highest;
double next;
if (in >> next) highest = next;
else return 0;
while (in >> next)
if (next > highest) highest = next;
return highest;
}
int main()
{ double max;
string input;
cout << "Do you want to read from a file? (y/n) ";
cin >> input;
if (input == "y")
{ string filename;
cout << "Please enter the data file name: ";
cin >> filename;
ifstream infile;
infile.open(filename.c_str());
if (infile.fail())
{ cout << "Error opening " << filename << "\n";
return 1;
}
max = read_data(infile);
infile.close();
}
else max = read_data(cin);
cout << "The maximum value is " << max << "\n";
return 0;
}
