5. Наследяване
 Производни
класове.
Производни
класове.
Наследяването е механизъм за разширяване на вече
съществуващи класове. Новият клас наследява съществуващия, като в
него се добавят нови членове-функции и полета с данни.
Базов клас (общ):
class Employee {
public:
Employee(string emp_name,
double init_salary);
void set_salary(double
new_salary);
string get_name() const;
double get_salary() const;
void print() const;
private:
string name;
double salary;
};
Производен клас
(специализиран):
class Manager : public Employee {
public:
Manager(string n, double
sal, string dept);
string get_department()
const;
void print() const;
private:
string department;
};
Обект от производния клас е
обект и от базовия клас; обратното не е вярно.
Конструиране на обект от
производния клас:
Manager man("Nino", 670, "Computer
Science");
Извикване на член-функция
от базовия
клас:
man.set_salary(1200);
Извикване на член-функция
от производния
клас:
cout << man.get_department();
Данните в производния
клас:
Manager
Employee
string name;
double salary;
|
string department;
|
|
man
|
Employee
"Computer Science"
|
|
Employee - базов
клас, Manager -
производен клас
- членовете на базовият клас са членове и на производния клас
(всеки обект от производния клас съдържа данните на базовия клас);
- функциите на производният клас нямат достъп до частните
членове на базовия клас .
 Дефиниции на
функции от производния клас.
Дефиниции на
функции от производния клас.
Конструкторът на производния клас има две
задачи:
- да инициализира полетата с данни;
- да инициализира обекта от базовия клас, който се съдържа в
производния клас.
Manager::Manager(string n,
double sal, string dept)
:
Employee(n, sal)
{ department = dept; }
Ако в базовия и в производния класове има
функции с едно и също име, то викането на член-функция на базовия
клас от функция на производния клас става с помощта на операция
"принадлежност към клас" - ::
void Manager::print()
{ Employee::print();
cout <<
department; }
Пример. Да се изобразят няколко часовника, които
показват часа в различни градове по света.
Да напишем най-напред базовия клас Clock за показване на
локалното време по два начина - нормалния (military) и американския
(am/pm).
// clock1.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#include "ccc_time.h"
class Clock {
public:
/**
Constructs a clock that can tell the local time.
@param use_military true if the clock uses military format (21:05) and
flase if the clock uses "am/pm" format (9:05 pm)
*/
Clock(bool use_military);
/**
Gets the location of this clock.
@return the location
*/
string get_location() const;
/**
Gets the hours of this clock.
@return the hours, in military or am/pm format
*/
int get_hours() const;
/**
Gets the minutes of this clock.
@return the minutes
*/
int get_minutes() const;
/**
Checks whether this clock uses miltary format.
@return true if miltary format
*/
bool is_military() const;
private:
bool military;
};
Clock::Clock(bool use_military)
{ military = use_military; }
string Clock::get_location() const
{ return "Local"; }
int Clock::get_hours() const
{ Time now;
int hours = now.get_hours();
if (military) return hours;
if (hours == 0) return 12;
else if (hours > 12) return hours - 12;
else return hours;
}
int Clock::get_minutes() const
{ Time now;
return now.get_minutes();
}
bool Clock::is_military() const
{ return military; }
int main()
{ Clock clock1(true);
Clock clock2(false);
bool more = true;
while (more)
{ cout << "Military time: "
<< clock1.get_hours() << ":"
<< setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clock1.get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n";
cout << "am/pm time: "
<< clock2.get_hours() << ":"
<< setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clock2.get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n";
cout << "Try again? (y/n) ";
string input;
getline(cin, input);
if (input != "y") more = false;
}
return 0;
}
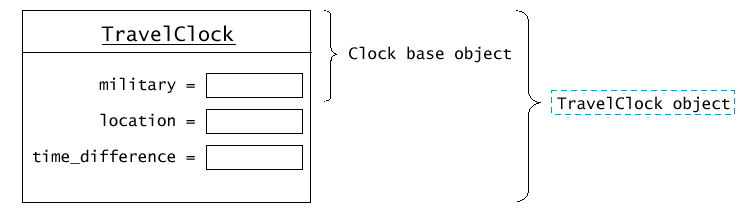
Сега в производния клас TravelClock добавяме две полета с
данни - location и time_difference. Времето на
друго място, се получава, като към местното време се добави
разликата, получена от различните часови зони. Например:
TravelClock clock("London", -2);
cout << "The time in " << clock.get_location() << " is "
<< clock.get_hours() << ":" << clock.get_minutes();
Обект от TravelClock има 3 разлики с обект от Clock:
- двете полета с данни: location и
time_difference;
- функцията get_hours добавя
разликата в часовите зони;
- функцията get_location връща името на мястото, а не
низа "Local".
class TravelClock : public Clock {
public:
TravelClock(bool mil, string loc, double off);
int get_hours() const;
string get_location() const;
private:
string location;
int time_difference;
};
Конструкторът на производния клас има две задачи:
- да инициализира полетата с данни;
- да инициализира обекта от базовия клас, който се съдържа в
производния клас.
TravelClock::TravelClock(bool mil, string loc, int diff)
: Clock(mil)
{ location = loc;
time_difference = diff;
while (time_difference < 0)
time_difference = time_difference + 24;
};
Ако не се извика конструктора на базовия клас, обектът от
производния клас се създава като автоматично (неявно) се вика
конструктора по подразбиране на базовия клас. Ако такъв конструктор
няма, то задължително трябва да вика явно конструктора на
базовия клас.
Забележка: Когато дефинираме клас и не
дефинираме конструктор, то автоматично се дефинира конструктор по
подразбиране с празен блок. Ако обаче дефинираме поне един
конструктор, то този коструктор с празен блок не се дефинира
автоматично.
Нека B::f е функция в базовия клас.
Производният D клас може да:
- разшири B::f като дефинира D::f
в производния клас, използвайки дефиницията в базовия клас. Например
TravelClock::get_hours е разширение на Clock::get_hours;
- замести B::f с нова D::f, дефинирана в
производния клас и независима от нея. Например TravelClock::get_location
замества Clock::get_location;
- наследи функцията B::f от базовия клас, без да я
дефинира отново. Например TravelClock наследява Clock::get_minutes
и Clock::is_military.
Член-функция може да се извика без неявен параметър -
когато се извика с неявен параметър (обект) от производен клас, т.е.
в блок на функция от производния клас.
int TravelClock::get_hours() const
{ . . .
if (is_military()) /* clock uses
military time */
return (h + time_difference) % 24;
. . .
}
Когато в базовия и в производния клас има функции с едно и също
име, то за да извикаме функцията от базовия клас в блок на функция
от производния клас, трябва да използваме операция "принадлежност
към клас" - ::, за да избегнем рекурсията.
int TravelClock::get_hours() const
{ . . .
int h = Clock::get_hours(); /* calls base-class function */
. . .
}
Данните на базовия клас (military) не са достъпни от
член-функциите на производния клас.
// clock2.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#include "ccc_time.h"
class Clock {
public:
Clock(bool use_military);
string get_location() const;
int get_hours() const;
int get_minutes() const;
bool is_military() const;
private:
bool military;
};
Clock::Clock(bool use_military)
{ military = use_military; }
string Clock::get_location() const
{ return "Local"; }
int Clock::get_hours() const
{ Time now;
int hours = now.get_hours();
if (military) return hours;
if (hours == 0) return 12;
else if (hours > 12) return hours - 12;
else return hours;
}
int Clock::get_minutes() const
{ Time now;
return now.get_minutes();
}
bool Clock::is_military() const
{ return military; }
class TravelClock : public Clock {
public:
/**
Constructs a travel clock that can tell the time
at a specified location
@param mil true if the clock uses military format
@param loc the location
@param diff the time difference from the local time
*/
TravelClock(bool mil, string loc, int diff);
string get_location() const;
int get_hours() const;
private:
string location;
int time_difference;
};
TravelClock::TravelClock(bool mil, string loc, int diff)
: Clock(mil)
{ location = loc;
time_difference = diff;
while (time_difference < 0)
time_difference = time_difference + 24;
}
string TravelClock::get_location() const
{ return location; }
int TravelClock::get_hours() const
{ int h = Clock::get_hours();
if (is_military())
return (h + time_difference) % 24;
else
{ h = (h + time_difference) % 12;
if (h == 0) return 12;
else return h;
}
}
int main()
{ Clock clock1(true);
TravelClock clock2(true, "Rome", -1);
TravelClock clock3(false, "Tokyo", 5);
cout << clock1.get_location() << " time: "
<< clock1.get_hours() << ":"
<< setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clock1.get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n";
cout << clock2.get_location() << " time: "
<< clock2.get_hours() << ":"
<< setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clock2.get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n";
cout << clock3.get_location() << " time: "
<< clock3.get_hours() << ":"
<< setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clock3.get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n";
return 0;
}
 Полиморфизъм
Полиморфизъм
Може да дефинираме вектор от часовници и да използваме цикъл за
показване на часа.
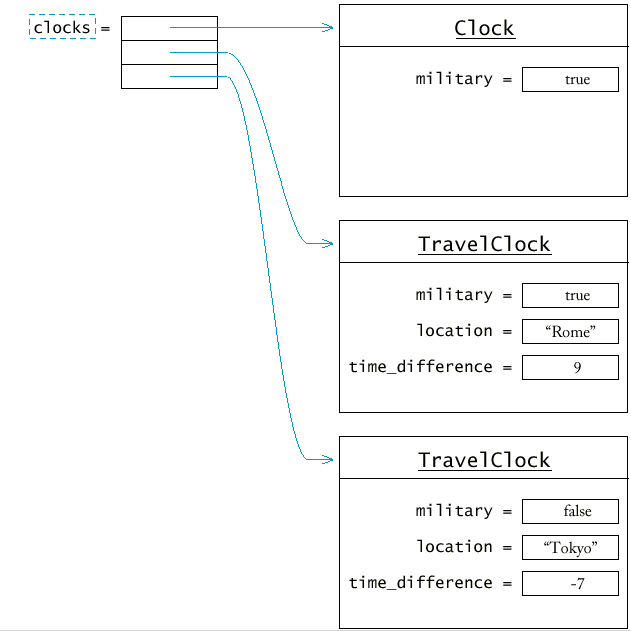
vector<Clock> clocks(3);
/* populate clocks */
clocks[0] = Clock(true);
clocks[1] = TravelClock(true, "Rome", -1);
clocks[2] = TravelClock(false, "Tokyo", 5);
for (int i = 0; i < clocks.size(); i++)
cout << clocks[i].get_location() << " time: "
<< clocks[i].get_hours() << ":"
<< setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clocks[i].get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n";
Тъй като обект от производния клас е обект и от
базовия клас, то можем да използваме операция присвояване с ляв
аргумент обект от Clock и десен аргумент - обект от
TravelClock. Ефектът обаче е отрязване на даните,
дефинирани в производния клас, т.е. на location и time_difference.
[ clocks2a.cpp
]
Може да използваме указатели към базовия клас за
елементи на вектора, тъй като указател от базов клас може да сочи
обект от производен клас (обратното не е вярно). Указателите от
различни класове имат една и съща дължина.
vector<Clock*> clocks(3);
/* populate clocks */
clocks[0] = new Clock(true);
clocks[1] = new TravelClock(true, "Rome", -1);
clocks[2] = new TravelClock(false, "Tokyo", 5);
for (int i = 0; i < clocks.size(); i++)
cout << clocks[i]->get_location() << " time: "
<< clocks[i]->get_hours() << ":"
<< setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clocks[i]->get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n";
Векторът clocks съдържа колекция от различни
часовници. Такава колекция се нарича полиморфна.
[ clocks2b.cpp
]
Резултатът от новия вариант е същия:
Local time is 21:15
Local time is 21:15
Local time is 9:15
защото указателите са от базовия клас и съответно с тях се вика
функция от същия клас. Това свързване на обект (неявен параметър) и
член-функция се нарича статично свързване. В С++ може да се
реализира и динамично свързване - когато се вика функция от
класа, от който е обектът, към който сочи указателя. За това
динамично свързване е необходимо функциите да се обяват като виртуални.
class Clock {
public:
Clock(bool use_military);
virtual string get_location() const;
virtual int get_hours() const;
int get_minutes() const;
bool is_military() const;
private:
. . .
};
Ето реализация на цялата програма с динамично свързване:
// clock3.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#include "ccc_time.h"
class Clock {
public:
Clock(bool use_military);
virtual string get_location() const;
virtual int get_hours() const;
int get_minutes() const;
bool is_military() const;
private:
bool military;
};
Clock::Clock(bool use_military)
{ military = use_military; }
string Clock::get_location() const
{ return "Local"; }
int Clock::get_hours() const
{ Time now;
int hours = now.get_hours();
if (military) return hours;
if (hours == 0) return 12;
else if (hours > 12) return hours - 12;
else return hours;
}
int Clock::get_minutes() const
{ Time now;
return now.get_minutes();
}
bool Clock::is_military() const
{ return military; }
class TravelClock : public Clock {
public:
TravelClock(bool mil, string loc, int diff);
string get_location() const;
int get_hours() const;
private:
string location;
int time_difference;
};
TravelClock::TravelClock(bool mil, string loc, int diff)
: Clock(mil)
{ location = loc;
time_difference = diff;
while (time_difference < 0)
time_difference = time_difference + 24;
}
string TravelClock::get_location() const
{ return location; }
int TravelClock::get_hours() const
{ int h = Clock::get_hours();
if (is_military())
return (h + time_difference) % 24;
else
{ h = (h + time_difference) % 12;
if (h == 0) return 12;
else return h;
}
}
int main()
{ vector<Clock*> clocks(3);
clocks[0] = new Clock(true);
clocks[1] = new TravelClock(true, "Rome", -1);
clocks[2] = new TravelClock(false, "Tokyo", 5);
for (int i = 0; i < clocks.size(); i++)
{ cout << clocks[i]->get_location() << " time: "
<< clocks[i]->get_hours() << ":"
<< setw(2) << setfill('0')
<< clocks[i]->get_minutes()
<< setfill(' ') << "\n";
}
return 0;
}

