#include "ccc_time.h"
Time sometime;
The shorthand in this very common situation is:Time day_end = Time(23, 59, 59); /* the last second of the day */
Time day_end(23, 59, 59); /* the last second of the day */
Time now; /* the time this object is created */
Time later(); /* NO! */
now.get_seconds(); /* returns the seconds value of now */
now.get_minutes(); /* returns the minutes value of now */
now.get_hours(); /* returns the hours value of now */
now.set_hours(2); /* NO! Not a supported member function */
now.set_hours(9999); /* NO! Doesn't make sense */
now.add_seconds(1000); /* Changes now to move by 1000 seconds */
now.seconds_from(day_end); /* Computes number of seconds between now and day_end */
long operator-(Time a, Time b)
{ return a.seconds_from(b);
}
Time now;
Time morning(9, 0, 0);
long seconds_elapsed = now - morning;
long seconds_elapsed = operator-(now, morning);
|
Syntax 17.1: Overloading Operator Definition return_type operatoroperator_symbol(parameters)
|
some_return_type operator+(Time a, Time b);
Time operator+(Time a, int sec)
{ Time r = a;
r.add_seconds(sec);
return r;
}
Time now;
Time later = now + 60; /* 60 seconds later */
bool operator==(Time a, Time b)
{ return a.seconds_from(b) == 0;
}
bool operator!=(Time a, Time b)
{ return a.seconds_from(b) != 0; // return !(a == b)
}
bool operator<(Time a, Time b)
{ return a.seconds_from(b) < 0; // return a - b < 0
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, Time a)
{ out << a.get_hours() << ":";
if (a.get_minutes() < 10) out << "0";
out << a.get_minutes() << ":";
if (a.get_seconds() < 10) out << "0";
out << a.get_seconds();
return out;
}
cout << now << "\n";
really means
(cout << now) << "\n";
that is
operator<<(cout, now) << "\n";
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Time& a)
{ int hours;
int minutes;
int seconds;
in >> hours >> minutes >> seconds;
a = Time(hours, minutes, seconds);
return in;
}
++x;
x++;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
vector<double> s(10);
double a = s[i++]; /* a is s[0], i is 1 */
double b = s[++j]; /* b is s[1], j is 1 */
void operator++(Time& a) /* prefix operator */
. . .
void operator++(Time& a, int dummy) /* postfix operator */
bool operator==(Time a, Time b); /* a == b means operator==(a,b) */
bool Time::operator==(Time b) const /* a == b means a.operator==(b) */
{ return seconds_from(b) == 0;
}
bool Time::operator!=(Time b) const
{ return !(*this == b); /* calls operator==(b) */
}
Time Time::operator++() /* prefix operator */
{ *this = *this + 1; /* calls operator+(1) */
return *this;
}
Time Time::operator++(int dummy) /* postfix operator */
{ Time t = *this;
*this = *this + 1; /* calls operator+(1) */
return t;
}
class Department {
...
private:
string name;
Employee* receptionist;
};
Department::Department(string n, Employee e)
{ name = n;
receptionist = new Employee(e.get_name(), e.get_salary());
}
/* second constructor */
Department::Department(string n)
{ name = n;
receptionist = NULL;
}
Department::~Department()
{ delete receptionist;
}
|
Syntax 17.2: Destructor Definition Class_name::~Class_name()
|
{ Department dept;
...
} // dept.~Department() automatically invoked here
...
Department* p = new Department(...);
...
delete p; // p->~Department() automatically invoked here
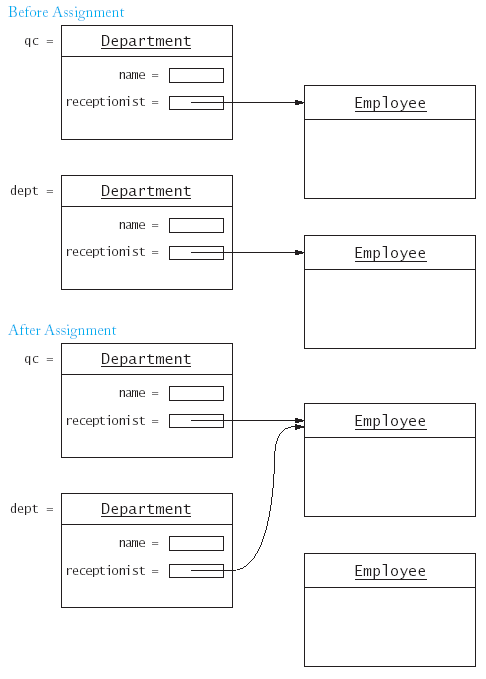
Department qc("Quality Control", Employee("Tester, Tina", 50000));
Department dept("Shipping", Employee("Hacker, Harry", 35000));
dept = qc;
Department& Department::operator=(const Department& b)
{ if (this != &b)
{ name = b.name;
delete receptionist;
if (b.receptionist == NULL) receptionist == NULL;
else
receptionist = new Employee(b.receptionist->get_name(),
b.receptionist->get_salary());
}
return *this;
}
z = y = x; // equivalent to z = (y = x) and z = y.operator=(x)
Department dept = qc; // not assignment operator!
Department dept(qc);
Department::Department(const Department& b)
{ name = b.name;
if (b.receptionist == NULL) receptionist = NULL;
else
receptionist = new Employee(b.receptionist->get_name(),
b.receptionist->get_salary());
}